WHAT IS NEUROTHERAPY?
Neurotherapy is focused on enhancing brain function. This holistic, evidence-based approach uses advanced technologies to provide very mild stimulation—through electrical currents, magnetic fields, or light therapy—to help optimize your brain. At its core, neurotherapy aims to support better mental, emotional, and cognitive health by directly influencing the brain’s natural activity patterns.
Neurotherapy is also sometimes referred to as “neuromodulation” - both are umbrella terms referring to a range of interventions designed to influence and improve brain functioning. This may include techniques like transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), and related methods that can safely and non-invasively alter activity in your brain’s neural networks when administered by trained professionals.
How does Neurotherapy work?
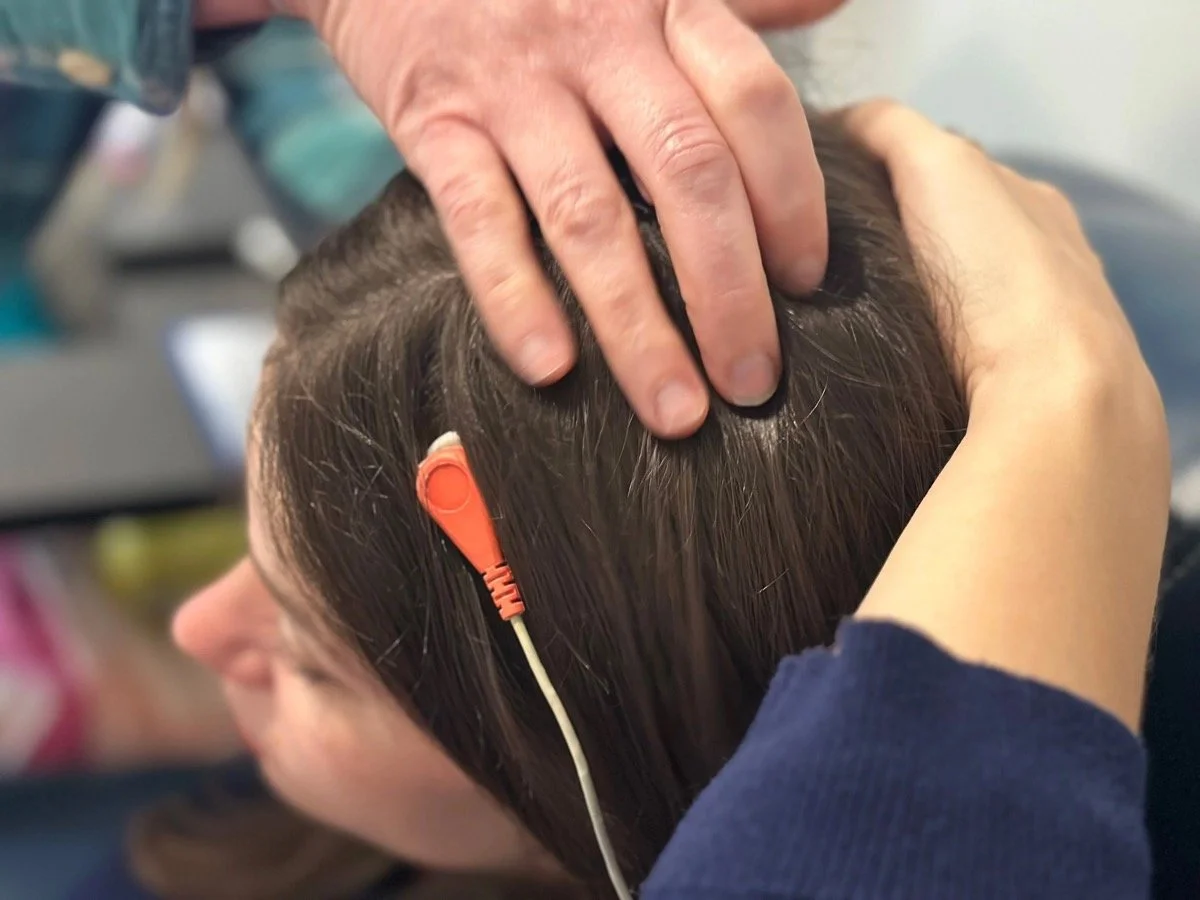
Neurotherapy starts with an individualized assessment, often using EEG to map brain patterns and identify areas of dysregulation or inefficiency.
Treatment sessions use neuromodulation technology to deliver gentle electrical stimulation to specific brain regions, aiming to “train” the brain much like exercising muscles.
The process is typically repeated over multiple sessions—many clients notice benefits such as improved mood, focus, or sleep within the first several treatments, but long-term change usually develops after 10-20 sessions.
These techniques can be used alone or in combination with medication and psychotherapy, often resulting in better outcomes than any single approach on its own.
THE GOAL OF NEUROTHERAPY IS FOR YOUR BRAIN TO BE BALANCED AND HOLD THIS NEW PATTERN INDEPENDENTLY! WE WANT YOU TO GET REAL RESULTS AND THE BEST BANG FOR YOUR BUCK.
Exploring the Types of Neurotherapy
There are several ways to support the brain’s natural ability to regulate and adapt. At Transformative Neurotherapy, we offer a range of evidence-based modalities, designed to target specific aspects of brain function. Every approach is selected and personalized to your unique goals and EEG data.
Learn more about the different types of neurotherapy we provide below.
Are there any side effects or safety concerns?
Neurotherapy is considered safe when practiced by certified clinicians, with most side effects being mild and temporary (such as minor skin irritation, fatigue, or mild headaches).
Neurotherapy is safe for adults and children. We often see children struggling in school with ADHD, where neurotherapy can be incredibly helpful for creating regulation and balance to help a child focus.
It is used to support a wide range of conditions, including anxiety, depression, addiction, ADHD, and other neurodevelopmental or mental health challenges.
-
Neurostimulation or Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS), is an active intervention utilizing the addition of a stimulus to entrain the brain to produce certain wavelengths, increase energy, or reduce inflammation utilizing a variety of technologies including:
tECS (Transcranial electrical stimulation) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique that passes an electrical current through the cortex of the brain to alter brain function. This innovative approach encompasses several modalities, including transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS), and Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS). The technique operates at subthreshold levels, modifying neuronal excitability without directly triggering action potentials
tDCS (Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation) tDCS is a non-invasive treatment for modulating brain activity with minimal side effects. It uses very low levels of electrical currents applied to the scalp that targets specific areas of the brain in order to enhance brain activity, often producing profound results. tDCS enhances rehabilitation in neurological conditions by promoting neuroplasticity and improving motor/speech function when combined with therapy.
tACS (Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation) is similar to tDCS as a neuromodulatory technique, but instead of applying a direct electrical current, tACS oscillates a sinusoidal current at a chosen frequency to interact with the brain’s natural cortical oscillations.
Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS): from basic mechanisms towards first applications in psychiatry | SpringerLinktRNS (Transcranial Random Noise) or Noise/ Acoustic therapy is a non-invasive noise stimulation that can increase synchronization of neural firing by amplifying the oscillatory activity and reducing the amount of internal noise particularly in the Brown Noise and Pink Noise frequencies. If a signal is too weak to induce action potential generation and random noise is added, the improvement of the signal can lead to enhanced cognitive performance.
Random noise stimulation in the treatment of patients with neurological disorders - PMC
VNS (Vagus Nerve Stimulation) The vagus nerve is the longest in the body and controls various functions including digestion, heart rate, breathing, and the immune system. When activated, the VNS device generates low-energy electrical signals, transmits these signals through the vagus nerve which disperses these signals to different areas of the brain. This process alters brain cell activity, potentially calming areas of abnormal electrical hyperactivity.
-
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (pEMF) has been around for decades and has been used by scientists around the world to study the effects of pEMF on organs and disease in the body. There are over 2,000 published clinical studies that show the benefit of pEMF on many different conditions. NeuroField’s FDA approved device is an ultra-low intensity, pulsed electromagnetic field (pEMF) unit that works to replenish energy and reduce stress in the brain and body. pEMF is purely electromagnetic and does not introduce direct current to the skin. The brain and body will “mimic” the pEMF fed into it and capillary blood flow will increase. Inflammation can limit the success of other types of biofeedback, pEMF can reduce inflammation and be given at fast speeds without generating heat and damaging tissue. pEMF can be used to entrain the brain via Operant conditioning or dis-entrain the brain via de habituation.
NeuroField’s pEMF has been documented as an intervention for insomnia, Parkinson’s disease, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, attention deficit disorder, anxiety, conduct disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder. It has been shown in clinical studies to be an effective intervention for many other conditions and symptoms. Follow-up with the subjects of the studies and the clinical population has suggested that the changes hold over time.
-
Photobiomodulation (PBM) is a form of neuromodulation using LED light therapy at various wavelengths, typically Red Light Therapy (RLT) or Near Infrared Light Therapy (NIR) to improve brain functioning. NIR therapy is a type of phototherapy that uses light in the near-infrared spectrum to promote healing and reduce inflammation. It's a non-invasive treatment that can be used for a variety of conditions, including skin rejuvenation, pain management, and even some neurological conditions. Numerous research studies confirm the benefits of light therapy in treating many mental health and physical conditions including depression, anxiety and even Alzheimer's. In essence, red light therapy eliminates that lack of energy that accompanies low mood and anxiety. Red light therapy is known to increase the efficacy and integrity of mitochondria – the ‘powerhouse’ of the cell. This energy is then distributed where it is needed the most. One of the ways NIR may support your mental health is by stimulating areas of the brain that are linked to certain types of depression and anxiety. Namely, dlPFC and vmPFC play critical roles in the pathophysiology of depression. With well-calculated exposure to RLT and NIR, it is possible to modulate appropriate brain areas, so you can treat and improve the depression and anxiety symptoms.